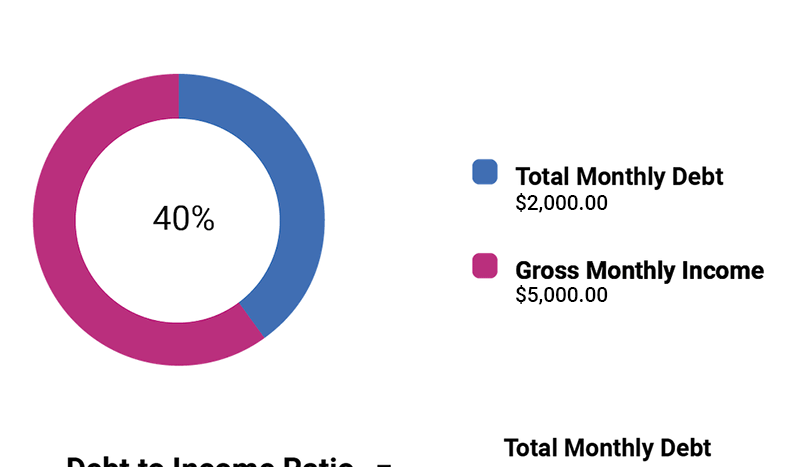
Debt-to-Income ratio
The house payment to income ratio, also known as the debt-to-income ratio, is a key metric used in the real estate industry to evaluate a borrower’s ability to repay a mortgage loan. It measures the percentage of a borrower’s income that goes towards paying their housing-related expenses, including mortgage payments, property taxes, insurance, and other related costs.
The house payment to income ratio is a crucial factor that affects both individual borrowers and the overall economy in the real estate industry. For borrowers, a high house payment to income ratio indicates that they may be at a higher risk of defaulting on their mortgage payments, which can lead to foreclosure, and can have significant long-term financial consequences.
On a larger scale, the house payment to income ratio is an important indicator of the overall health of the real estate market and the broader economy. When the ratio is high, it can signal that home prices have risen to levels that may be unaffordable for many potential buyers, resulting in a slowdown in the housing market.
Conversely, a low house payment to income ratio can indicate that home prices are more affordable, which can encourage more people to enter the housing market, leading to increased demand and higher home prices. This can stimulate economic growth and contribute to the overall health of the real estate market and the broader economy.
The house payment to income ratio can also be affected by the state of the economy. During times of economic recession or instability, unemployment rates may rise, and many people may experience a decrease in income. This can result in a higher house payment to income ratio, as people may be struggling to make their mortgage payments.
Similarly, changes in interest rates can also affect the house payment to income ratio. When interest rates are low, the cost of borrowing is less expensive, making homeownership more affordable for many potential buyers. However, when interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing increases, leading to higher mortgage payments and a higher house payment to income ratio.
Overall, the house payment to income ratio is a key metric used by lenders, real estate agents, and potential homebuyers to evaluate the affordability of housing. It can have significant impacts on both individual borrowers and the broader economy, and it’s essential to monitor changes in the ratio over time to make informed decisions about buying or selling real estate.
Lebanon has been facing a severe economic crisis since 2019, which has had a significant impact on the real estate market in the country. The crisis has resulted in a sharp devaluation of the Lebanese pound and a significant decrease in the purchasing power of Lebanese citizens, which has made it difficult for many people to afford their housing-related expenses.
As a result of the economic crisis, the house payment to income ratio has increased significantly in Lebanon. This increase has made it more challenging for many potential homebuyers to afford a mortgage, leading to a decrease in demand for real estate. According to some reports, the real estate market in Lebanon has experienced a decline of up to 50% in sales and a drop in prices of up to 70%.
The economic crisis in Lebanon has also had a severe impact on the construction industry. Many construction projects have been delayed or cancelled due to the lack of funding, and many developers have been unable to secure financing for new projects. This has led to a decrease in the supply of new housing units, which has further affected the real estate market.
Furthermore, the crisis has also led to an increase in the number of properties for rent as many people have been unable to afford to buy a home. This increase in the supply of rental properties has resulted in a decrease in rental prices, making it more affordable for renters to find a suitable home, especially if you are paying by dollar. As most mortgages in Lebanon were denominated in US dollars, meant that as the value of the Lebanese pound declined, the cost of servicing these mortgages increased, making it increasingly difficult for borrowers to meet their debt obligations if they are to repay these in dollars. But that was not the case.
As the value of the Lebanese pound declined, the cost of servicing US dollar-denominated mortgages increased significantly. However, those who held US dollars were able to take advantage of the devaluation and pay off their mortgages with a fraction of the cost, as the US dollar’s value remained relatively stable. This phenomenon has been observed in other countries with volatile currencies and high inflation rates, where those who held reserve currencies were able to benefit from the devaluation of the local currency.
While this may have been beneficial for those who were able to take advantage of the situation, it has had a mixed impact on the real estate market and the banking sector. On the one hand, the ability of some homeowners to pay off their mortgages has reduced the amount of non-performing loans in the banking sector and may have helped stabilize the market to some extent. On the other hand, the decreased demand for new mortgages has further weakened the financial position of the banking sector and contributed to a reduction in the supply of new housing units.
The ability of some Lebanese citizens who held US dollars to pay off their mortgages with a fraction of the cost has reduced the amount of non-performing loans in the banking sector. This is because the banks have been able to recover some of the debt that would have otherwise been lost, which could have had negative implications for the stability of the banking system.
However, with the devaluation of the Lira and the decreased demand for new mortgages has had a negative impact on the real estate market and the banking sector combined. With almost no one seeking new mortgages, the financial position of the banking sector has been further weakened, as the banks have been unable to generate new revenue streams by lending to new borrowers. Additionally, the reduced demand for housing, and paying primarily in cash has contributed to a reduction in the supply of new housing units, which may have further undermined the health of the real estate market.
Moreover, the overall impact of the crisis on the real estate market and the banking sector has been severe. The banking sector, which was once considered the backbone of the Lebanese economy, has suffered significant losses due to the crisis. The value of non-performing loans and other debt on the balance sheets of many banks has increased, which has put pressure on their capital reserves and their ability to lend.
The real estate market has also been severely affected by the crisis, with property prices falling significantly in many areas of the country. This has made it more difficult for many people to sell their homes, and has also led to a reduction in the supply of new housing units. Moreover, the crisis has led to significant social and economic hardship for many people, who have been unable to access their savings or afford housing-related expenses.
But if history tells us anything in Lebanon, is that the economy always rebounds. Any investment today will have a large revenue when the economy begins to stabilize. This is a long term investment strategy that will yield more income than any savings account or other investment.